March 9, 2023
GDP growth in the euro area and the EU
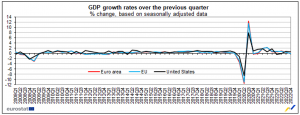
According to an estimate released by Eurostat, the European Union’s statistical office, seasonally adjusted GDP declined by 0.1% in the EU and stayed steady in the euro area in the fourth quarter of 2022 compared to the prior quarter. GDP in the EU and the euro region increased by 0.4% in the third quarter of 2022.
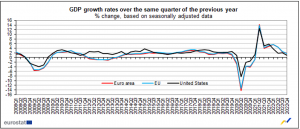
Seasonally adjusted GDP rose by 1.8% in the euro area and by 1.7% in the EU in the fourth quarter of 2022, following increases of +2.4% in the euro area and +2.6% in the EU in the prior quarter.
Following growth of +5.3% and +5.4% in the euro region and the EU, respectively, in 2021, GDP climbed by 3.5% overall in 2022.
The United States’ GDP increased by 0.7% in the fourth quarter of 2022 compared to the previous quarter (after increasing by +0.8% in the third quarter of 2022). After rising by 1.9% in the preceding quarter, GDP climbed by 0.9% when compared to the same quarter last year.
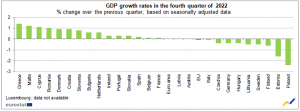
GDP growth by Member State
Greece (+1.4%), Malta (+1.2%), and Cyprus (+1.1%) had the highest GDP growth rates compared to the prior quarter. Poland (-2.4%), Estonia (-1.6%), and Finland (-0.6%) saw the largest drops.
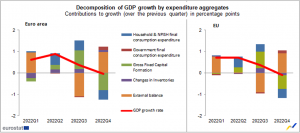
GDP components and contributions to growth
After increasing by 0.9% in the euro area and by 0.7% in the EU during the previous quarter, household final consumption expenditure declined by 0.9% in the euro area and by 0.8% in the EU during the fourth quarter of 2022. After declining by -0.2% in both regions the previous quarter, government final consumption expenditure climbed by 0.7% in the EU and the euro area. After increasing by 3.9% and 3.5%, respectively, gross fixed capital formation fell by 3.6% in the euro area and by 2.8% across the EU. After rising by 1.7% and +1.9%, exports in the euro area grew by 0.1% and stayed steady in the EU. Both the EU and the euro area saw a 1.9% decline in imports (following increases of 4.2% and 3.9% in the previous quarter, respectively).
Both in the EU and the euro area, household final consumption expenditure had a negative impact on GDP growth (-0.4 percentage points – pp in both zones). For both zones, the contributions from final government spending were positive (+0.2 percent for the euro area and +0.1 pp for the EU). Gross fixed capital formation had a negative contribution to the euro area (-0.8 pp) and the EU (-0.6 pp). The external balance made positive contributions (+1.0 pp for the euro region and +0.9 pp for the EU). The euro region (+0.1 percent) saw positive contributions from inventory adjustments, while the EU saw negative contributions (-0.1 pp).
GDP levels in the euro area and EU
Based on data that has been corrected for seasonality, GDP volumes in the EU and the euro area were 2.4% and 2.8%, respectively, higher than the levels seen in the fourth quarter of 2019—previous to the COVID-19 epidemic. The GDP for the US increased by 5.1% from the fourth quarter of 2019 levels.
Disclaimer:
Analyst Certification – The views expressed in this research report accurately reflect the personal views of Mayberry Investments Limited Research Department about those issuer (s) or securities as at the date of this report. Each research analyst (s) also certify that no part of their compensation was, is, or will be, directly or indirectly, related to the specific recommendation (s) or view (s) expressed by that research analyst in this research report.
Company Disclosure – The information contained herein has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable, however, its accuracy and completeness cannot be guaranteed. You are hereby notified that any disclosure, copying, distribution or taking any action in reliance on the contents of this information is strictly prohibited and may be unlawful. Mayberry may affect transactions or have positions in securities mentioned herein. In addition, employees of Mayberry may have positions and effect transactions in the securities mentioned here.
