December 12, 2023
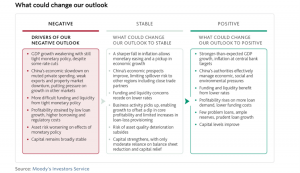
According to Moody’s Investor Service, the outlook for global banks for 2024 is negative as tighter monetary policies by central banks have resulted in lower GDP growth. The banking sector faces challenges with reduced liquidity and strained repayment capacity, adversely affecting loan quality and increasing asset risks. Profitability gains are expected to decrease due to higher funding costs, lower loan growth, and increased reserve buildups. Despite anticipated difficulties in funding and liquidity, capitalization is forecasted to remain stable. This stability is attributed to organic capital generation, moderate loan growth, and the capital buildup efforts of some of the largest US banks.
Moody’s highlighted the following:
- The operating environment will deteriorate under tight monetary policies. Major central banks will start to cut rates, but money will remain tight, resulting in lower GDP growth in 2024. Inflation is slowing, but geopolitical and climate risks remain. China ‘s (A1 stable) economic growth is set to slow on muted private spending, weak exports and an ongoing property market correction.
- Loan quality will be squeezed by low liquidity and tighter repayment capacity. Previous rate hikes will lead to greater asset risk and reserve buildups. Rising unemployment in advanced economies will weaken loan performance. Commercial real estate (CRE) exposure in the US and Europe is a growing risk; in Asia-Pacific, specific property markets face stress. Chinese banks face risks from slower economic growth and second-order impact from a prolonged property downturn.
- Profitability will fall on higher funding costs, lower loan growth and loan-loss provisioning needs. Profitability gains from the last two years will likely start to subside but remain sound. Higher funding costs will shrink net interest margins, while loan production will continue to weaken as rate hikes limit demand and credit standards tighten. Provisioning expenses will follow increases in asset risks, while operating expenses contend with rising tech-related investments and new regulatory costs.
- Funding and liquidity will be more challenging because of monetary policy tightening. Deposit growth will decelerate as deposits move to more expensive accounts or exit banking systems, while market funding increases. Lower loan growth will limit funding strains. Foreign currency shortages will strain liquidity in some frontier markets.
- Capital will remain broadly stable. Banks in Europe will maintain ample buffers above regulatory minimums. In the US (Aaa negative), some of the largest banks will build capital because of regulatory changes. In Asia-Pacific, organic capital generation and prudent dividends will allow capital stability.
Disclaimer:
Analyst Certification -The views expressed in this research report accurately reflect the personal views of Mayberry Investments Limited Research Department about those issuer (s) or securities as at the date of this report. Each research analyst (s) also certify that no part of their compensation was, is, or will be, directly or indirectly, related to the specific recommendation (s) or view (s) expressed by that research analyst in this research report.
Company Disclosure -The information contained herein has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable, however its accuracy and completeness cannot be guaranteed. You are hereby notified that any disclosure, copying, distribution or taking any action in reliance on the contents of this information is strictly prohibited and may be unlawful. Mayberry may effect transactions or have positions in securities mentioned herein. In addition, employees of Mayberry may have positions and effect transactions in the securities mentioned herein.
